Acute bronchitis is an infection of the bronchial tree. The bronchial tree is made up of the tubes 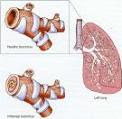 that carry air into your lungs. When these tubes get infected, they swell and mucus (thick fluid) forms inside them. This makes it hard for you to breathe.
that carry air into your lungs. When these tubes get infected, they swell and mucus (thick fluid) forms inside them. This makes it hard for you to breathe.
Acute bronchitis is bronchitis that lasts a short time (several weeks or less), while chronic bronchitis is bronchitis that is long-lasting or recurring (and is usually caused by constant irritation of the bronchial tree, such as from smoking).
Acute bronchitis is almost always caused by viruses that attack the lining of the bronchial tree and cause infection. As your body fights back against these viruses, more swelling occurs and more mucus is produced. It takes time for your body to kill the viruses and heal the damage to your bronchial tubes.
In most cases, the same viruses that cause colds cause acute bronchitis. Research has shown that bacterial infection is a much less common cause of bronchitis than doctors used to think. Very rarely, an infection caused by a fungus can cause acute bronchitis. Exposure to an irritant (such as smoke, dust or pollutants in the air) may cause bronchitis.
Most cases of acute bronchitis will go away on their own. It's a good idea to get plenty of rest, drink lots of noncaffeinated fluids (for example, water and fruit juices) and increase the humidity in your environment. Over-the-counter pain relievers can reduce inflammation, ease pain and lower fever. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (such as ibuprofen, naproxen and aspirin) help with pain and inflammation. Acetaminophen helps with pain and reducing fever.
It is okay to take an over-the-counter cough suppressant if your cough is dry (not producing any mucus). It's best not to suppress a cough that brings up mucus because this type of cough helps clear the mucus from your bronchial tree faster. Cough medicine is not recommended for children, especially those under 4 years of age.
Because acute bronchitis is usually caused by viruses, antibiotics do not help. Even if you cough up mucus that is colored or thick, antibiotics probably won’t help you get better any faster. However, if your doctor thinks your bronchitis is caused by a bacteria, he or she may prescribe antibiotics.
If you smoke, you should quit. This will help your bronchial tree heal faster.
Some people who have acute bronchitis need medicines that are usually used to treat asthma. If you hear yourself wheezing, this indicates you may need asthma medicines. These medicines can help open the bronchial tubes and clear out mucus. They are usually given with an inhaler. An inhaler sprays the medicine right into the bronchial tree. Your doctor will decide if this treatment is right for you.
 that carry air into your lungs. When these tubes get infected, they swell and mucus (thick fluid) forms inside them. This makes it hard for you to breathe.
that carry air into your lungs. When these tubes get infected, they swell and mucus (thick fluid) forms inside them. This makes it hard for you to breathe.Acute bronchitis is bronchitis that lasts a short time (several weeks or less), while chronic bronchitis is bronchitis that is long-lasting or recurring (and is usually caused by constant irritation of the bronchial tree, such as from smoking).
Acute bronchitis is almost always caused by viruses that attack the lining of the bronchial tree and cause infection. As your body fights back against these viruses, more swelling occurs and more mucus is produced. It takes time for your body to kill the viruses and heal the damage to your bronchial tubes.
In most cases, the same viruses that cause colds cause acute bronchitis. Research has shown that bacterial infection is a much less common cause of bronchitis than doctors used to think. Very rarely, an infection caused by a fungus can cause acute bronchitis. Exposure to an irritant (such as smoke, dust or pollutants in the air) may cause bronchitis.
Most cases of acute bronchitis will go away on their own. It's a good idea to get plenty of rest, drink lots of noncaffeinated fluids (for example, water and fruit juices) and increase the humidity in your environment. Over-the-counter pain relievers can reduce inflammation, ease pain and lower fever. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (such as ibuprofen, naproxen and aspirin) help with pain and inflammation. Acetaminophen helps with pain and reducing fever.
It is okay to take an over-the-counter cough suppressant if your cough is dry (not producing any mucus). It's best not to suppress a cough that brings up mucus because this type of cough helps clear the mucus from your bronchial tree faster. Cough medicine is not recommended for children, especially those under 4 years of age.
Because acute bronchitis is usually caused by viruses, antibiotics do not help. Even if you cough up mucus that is colored or thick, antibiotics probably won’t help you get better any faster. However, if your doctor thinks your bronchitis is caused by a bacteria, he or she may prescribe antibiotics.
If you smoke, you should quit. This will help your bronchial tree heal faster.
Some people who have acute bronchitis need medicines that are usually used to treat asthma. If you hear yourself wheezing, this indicates you may need asthma medicines. These medicines can help open the bronchial tubes and clear out mucus. They are usually given with an inhaler. An inhaler sprays the medicine right into the bronchial tree. Your doctor will decide if this treatment is right for you.